Review of recently reported Ricin detection techniques focusing on combined immunoassay detection with abrin and saxitoxin in human plasma
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37944/jams.v6i2.191Keywords:
biotoxin, ricin, abrin, prohibition of chemical weapons, immunoassay detection platformsAbstract
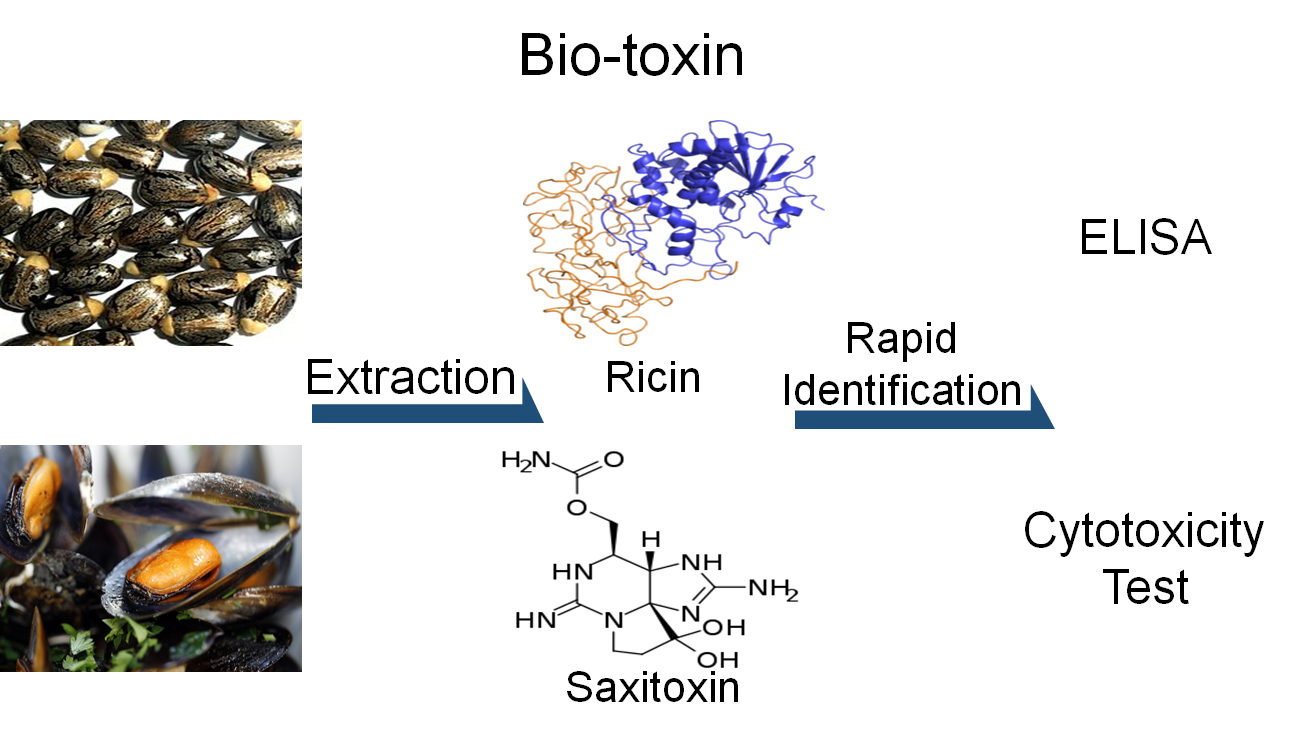
Increasing non-traditional threats from biological or chemical weapons, the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) have tried to perform the preliminary analysis of biotoxin sample to standardize analysis methods and strengthen analytical capabilities among OPCW member countries. With the changes of new analysis, ROK CBRN Defense Research Institute (CDRI) established enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and cytotoxicity analysis methods for ricin, abrin, and saxitoxin through the OPCW exercise on Biotoxin sample analysis. Thus, this study aims to established analytical methods (ELISA and cytotoxicity analysis) for the biological toxins called ricin, abrin and saxitoxin according to recent OPCW Biotoxin detection exercise. In particular, to refine practical and effective methods of biological analysis, we reviewed recent research on scientific analysis of ricin as a potential bioterror weapon, letter with ricin sent in White House, and suggested future agendas for preparedness testing.
Metrics
References
Andrinolo, D., Michea, L. F., & Lagos, N. (1999). Toxic effects, pharmacokinetics and clearance of saxitoxin, a component of paralytic shellfish poison (PSP), in cats. Toxicon, 37(3), 447-464. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0041-0101(98)00173-1
Audi, J., Belson, M., Patel, M., Schier, J., & Osterloh, J. (2005). Ricin poisoning: a comprehensive review. Jama, 294(18), 2342-2351. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.294.18.2342
Baldoni, A. B., Araújo, A. C. G., de Carvalho, M. H., Gomes, A. C. M., & Aragao, F. J. (2010). Immunolocalization of ricin accumulation during castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) seed development. International Journal of Plant Biology, 1(2), e12. https://doi.org/10.4081/pb.2010.e12
Bradberry, S. (2016). Ricin and abrin. Medicine, 44(2), 109-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpmed.2015.11.019
Doan, L. G. (2004). Ricin: mechanism of toxicity, clinical manifestations, and vaccine development. A review. Journal of Toxicology: Clinical Toxicology, 42(2), 201-208. https://doi.org/10.1081/CLT-120030945
Dubois, M., Demoulin, L., Charlier, C., Singh, G., Godefroy, S. B., Campbell, K., ... & Delahaut, P. (2010). Development of ELISAs for detecting domoic acid, okadaic acid, and saxitoxin and their applicability for the detection of marine toxins in samples collected in Belgium. Food Additives and Contaminants, 27(6), 859-868. https://doi.org/10.1080/1944004100 3662881
Endo, Y., & Tsurugi, K. (1987). RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain. Mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 262(17), 8128-8130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)47538-2
Franz, D.R. and Jaax, N.K. (1997). Ricin toxin. Medical aspects of chemical and biological warfare, 3, 631-642. Retrieved from https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=e64a5d775bb866fac096253a7aae8edab34c6780#page=634
Gatto-Menking, D. L., Yu, H., Bruno, J. G., Goode, M. T., Miller, M., & Zulich, A. W. (1995). Sensitive detection of biotoxoids and bacterial spores using an immunomagnetic electrocheminescence sensor. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 10(6-7), 501-507. https://doi.org/10.1016/0956-5663(95)96925-O
Hoyt, K., Barr, J. R., & Kalb, S. R. (2021). Detection of ricin activity and structure by using novel galactose-terminated magnetic bead extraction coupled with mass spectrometric detection. Analytical biochemistry, 631, 114364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2021.114364
Johnson, R. C., Zhou, Y., Statler, K., Thomas, J., Cox, F., Hall, S., & Barr, J. R. (2009). Quantification of saxitoxin and neosaxitoxin in human urine utilizing isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry. Journal of analytical toxicology, 33(1), 8-14. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/33.1.8
Kandasamy, K., Selvaprakash, K., & Chen, Y. C. (2019). Using lactosylated cysteine functionalized gold nanoparticles as colorimetric sensing probes for rapid detection of the ricin B chain. Microchimica Acta, 186, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3900-0
Liang, L. H., Yang, Y., Geng, S., Cheng, X., Yu, H. L., Liu, C. C., & Liu, S. L. (2021). Rapid differential detection of abrin isoforms by an acetonitrile-and ultrasound-assisted on-bead trypsin digestion coupled with LC-MS/MS analysis. Toxins, 13(5), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13050358
Long-Hui, L., Xi, C., Yang, Y., Long, Y., Hui-Lan, Y., Du-Bin, ... & Shi-Lei, L. (2021). An in Vitro Detection Method for Depurination Activity of Ricin Based on A Novel RNA Substrate and Its Application. CHINESE JOURNAL OF ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY, 49(10), 1694-1703. https://doi.org/10.19756/j.issn.0253-3820.211117
Lord, M. J., Jolliffe, N. A., Marsden, C. J., Pateman, C. S., Smith, D. C., Spooner, R. A., ... & Roberts, L. M. (2003). Ricin: mechanisms of cytotoxicity. Toxicological reviews, 22, 53-64. https://doi.org/10.2165/00139709-200322010-00006
Makdasi, E., Laskar, O., Milrot, E., Schuster, O., Shmaya, S., & Yitzhaki, S. (2019). Whole-cell multiparameter assay for ricin and abrin activity-based digital holographic microscopy. Toxins, 11(3), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11030174
Mechaly, A., Cohen, H., Cohen, O., & Mazor, O. (2016). A biolayer interferometry-based assay for rapid and highly sensitive detection of biowarfare agents. Analytical biochemistry, 506, 22-27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2016.04.018
Medlin, L. (2013). Molecular tools for monitoring harmful algal blooms. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20, 6683-6685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1195-3
Melati, L. T., Siahaan, T. ., & Putra Apriyanto, I. N. (2022). Biodefense against Abrin and Ricin as bioterrorism agents - a virtual screening of Indonesian plant medicinal properties. Defense and Security Studies, 3, 113-120. https://doi.org/10.37868/dss.v3.id217
Nagatsuka, T., Uzawa, H., Sato, K., Kondo, S., Izumi, M., Yokoyama, K., ... & Tamiya, E. (2013). Localized surface plasmon resonance detection of biological toxins using cell surface oligosaccharides on glyco chips. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 5(10), 4173-4180. https://doi.org/10.1021/am4002937
Olsnes, S. (2004). The history of ricin, abrin and related toxins. Toxicon, 44(4), 361-370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2004.05.003
Olsnes, S., Refsnes, K., & Pihl, A. (1974). Mechanism of action of the toxic lectins abrin and ricin. Nature, 249(5458), 627-631. https://doi.org/10.1038/249627a0
Pancrazio, J. J. (2007). Broadband detection of environmental neurotoxicants. In ACS Publications. Retrieved from https://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ac071994f
Pöhlmann, C., & Elßner, T. (2020). Multiplex immunoassay techniques for on-site detection of security sensitive toxins. Toxins, 12(11), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12110727
Schantz, E. J., Ghazarossian, V. E., Schnoes, H. K., Strong, F. M., Springer, J. P., Pezzanite, J. O., & Clardy, J. (1975). Structure of saxitoxin. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 97(5), 1238-1239. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00838a045
Silva, C. C. P., Zannin, M., Rodrigues, D. S., Santos, C. R. D., Correa, I. A., & Haddad Junior, V. (2010). Clinical and epidemiological study of 27 poisonings caused by ingesting puffer fish (Tetrodontidae) in the states of Santa Catarina and Bahia, Brazil. Revista do Instituto de Medicina Tropical de Sao Paulo, 52, 51-56. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0036-4665201
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Journal of Advances in Military Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

이 저작물은 크리에이티브 커먼즈 저작자표시 4.0 국제 라이선스에 따라 이용할 수 있습니다.






